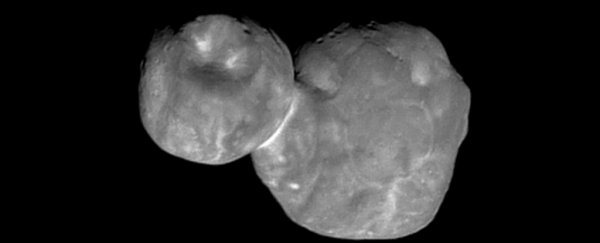
The most distant object our species has ever visited, a space rock called 2014 MU69, is less snowman-shaped than scientists previously thought.
NASA flew its New Horizons probe by the rock, which is nicknamed Ultima Thule and located 4 billion miles from Earth, on New Year's Day.
New Horizons flew within 2,200 miles of MU69, travelling at a speed of 32,200 mph. The flyby gave scientists the opportunity to collect photos and information about the rock that they hope will help solve some longstanding mysteries about the solar system's 4.5 billion years of history.
The first image the probe beamed back showed two reddish-coloured spherical segments on top of each other, like a snowman. Subsequent data revealed that the object flips like a giant hourglass.
But it will take about 20 months for New Horizons to send all of the images it captured back to Earth, and scientists' understanding of the rock is changing as fresh perspectives get revealed.
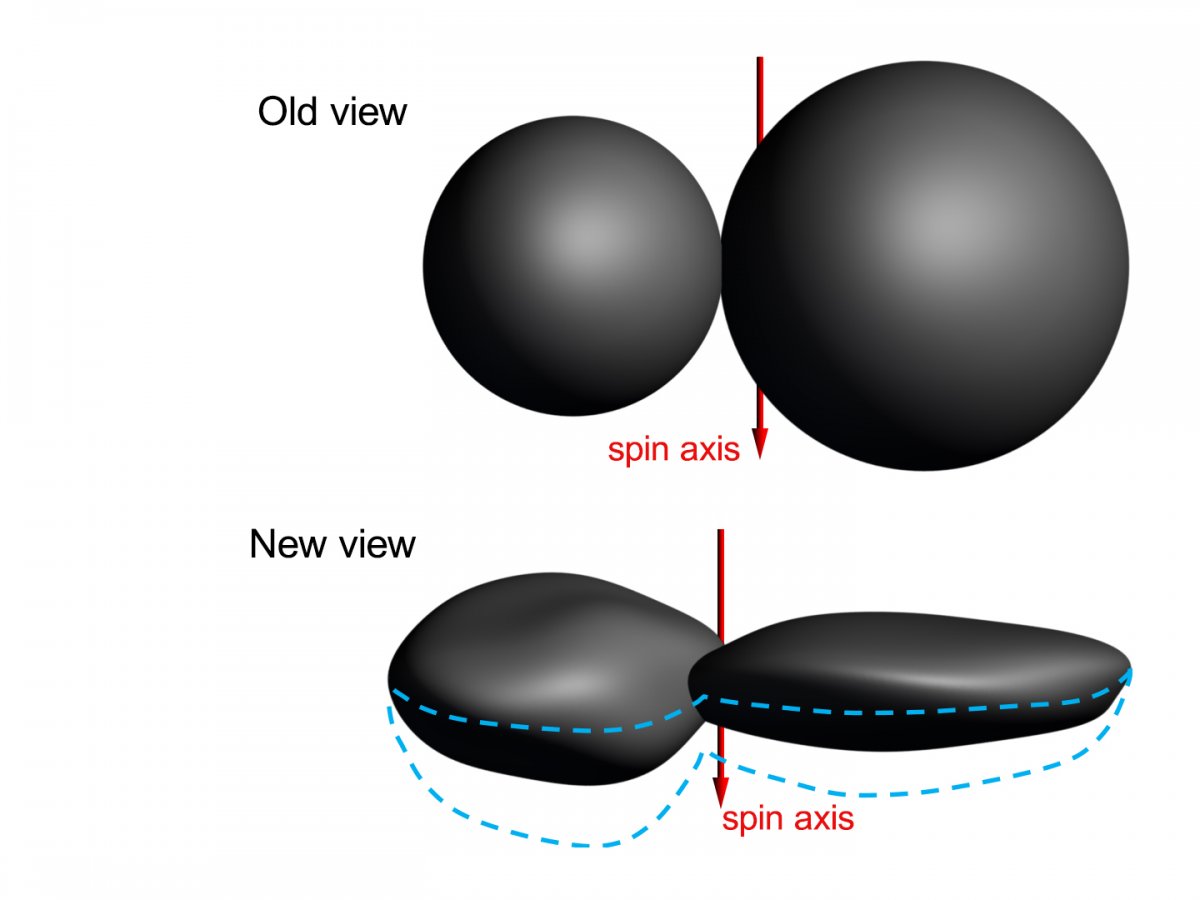
The newest sequence of images suggests that instead of two spheres, MU69's sections (called "lobes") are somewhat flat. The shape is relatively unprecedented in scientific observations of the solar system.
"We've never seen something like this orbiting the sun," Alan Stern, principal investigator on the New Horizons mission, said in a press release.
Based on the new images, the larger lobe (nicknamed Ultima) appears to more closely resemble a giant pancake. The smaller lobe (Thule) is akin to a dented walnut, NASA's New Horizons team reported.
 (NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/SwRI)
(NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/SwRI)
"We had an impression of Ultima Thule based on the limited number of images returned in the days around the flyby, but seeing more data has significantly changed our view," Stern said.
"It would be closer to reality to say Ultima Thule's shape is flatter, like a pancake. But more importantly, the new images are creating scientific puzzles about how such an object could even be formed."
NASA scientists shared the 3D animation of the space rock's shape below, which was created using images that New Horizons captured as it left MU69 behind. The photos were taken nearly 10 minutes after the probe passed its closest point to the rock.
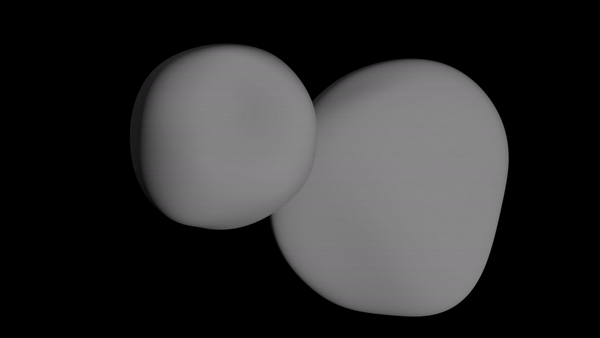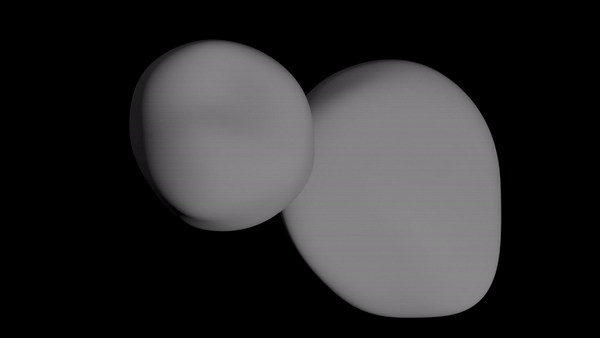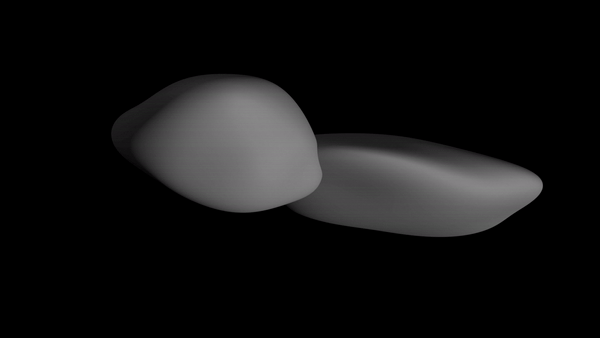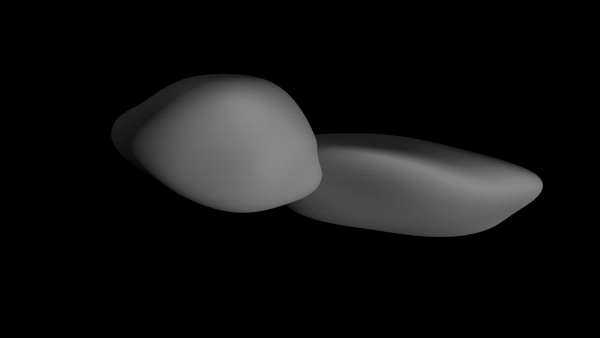 (NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/SwRI)
(NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/SwRI)
While these are far from the final photos of Ultima Thule that New Horizons will send back, they do represent the spacecraft's last glimpses of the rock as it streaked away.
This article was originally published by Business Insider.
More from Business Insider: