In recent years, an increasing number of scientific investigations have backed an alarming hypothesis: Alzheimer's disease may not be merely a condition of an aging brain, but the product of infection.
While the exact mechanisms of this infection are something researchers are still trying to isolate, numerous studies suggest the deadly emergence of Alzheimer's goes way beyond what we used to think.
One such study, published in 2019, suggested what could be one of the most definitive leads yet for a bacterial culprit behind Alzheimer's, and it comes from a somewhat unexpected quarter: gum disease.
Related: Microbes in Your Mouth May Impact Your Risk of Cognitive Decline
Watch the video below for a summary of their study:

In a paper led by senior author Jan Potempa, a microbiologist from the University of Louisville, researchers reported the discovery of Porphyromonas gingivalis – the pathogen behind chronic periodontitis (aka gum disease) – in the brains of deceased Alzheimer's patients.
It wasn't the first time the two factors have been linked, but the researchers went further.
In separate experiments with mice, oral infection with the pathogen led to brain colonization by the bacteria, together with increased production of amyloid beta (Aβ), the sticky proteins commonly associated with Alzheimer's.
Related: This Popular Diet Seems to Reduce Gum Disease, Scientists Say
The research team, coordinated by pharma startup Cortexyme, which was co-founded by first author Stephen Dominy, wasn't claiming to have discovered definitive evidence of Alzheimer's causation.
But it was clear they thought we had a strong line of investigation here.
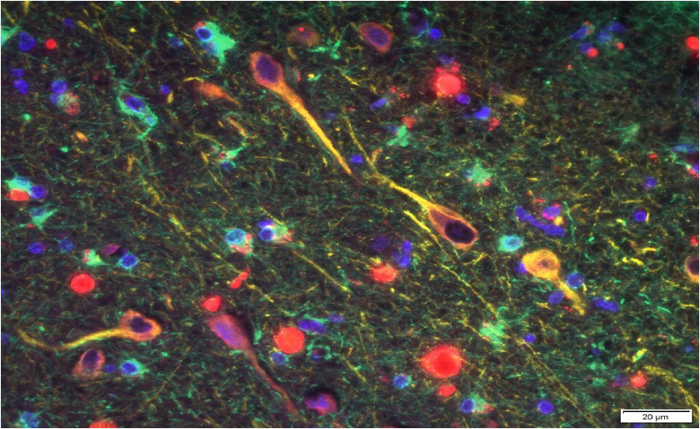
"Infectious agents have been implicated in the development and progression of Alzheimer's disease before, but the evidence of causation hasn't been convincing," Dominy said at the time.
"Now, for the first time, we have solid evidence connecting the intracellular, Gram-negative pathogen, P. gingivalis, and Alzheimer's pathogenesis."
In addition, the team identified toxic enzymes called gingipains secreted by the bacteria in the brains of Alzheimer's patients, which correlated with two separate markers of the disease: the tau protein, and a protein tag called ubiquitin.
Related: Stomach Ulcer Bacteria Could Be a Surprise Ally Against Alzheimer's
But even more compellingly, the team identified these toxic gingipains in the brains of deceased people who were never diagnosed with Alzheimer's.
That's important, because while P. gingivalis and the disease have been linked before, it's never been known – to put it simply – whether gum disease causes Alzheimer's, or whether dementia leads to poor oral care.
The fact that low levels of gingipains were evident even in people who were never diagnosed with Alzheimer's could be a smoking gun – suggesting they might have developed the condition if they had lived longer.
"Our identification of gingipain antigens in the brains of individuals with AD and also with AD pathology but no diagnosis of dementia argues that brain infection with P. gingivalis is not a result of poor dental care following the onset of dementia or a consequence of late-stage disease," the authors explained in their paper.
"But it is an early event that can explain the pathology found in middle-aged individuals before cognitive decline."
Further, a compound formulated by the company called COR388, showed in experiments with mice that it could reduce bacterial load of an established P. gingivalis brain infection, while also reducing amyloid-beta production and neuroinflammation.
We'll have to wait and see what future research will uncover about this link, but the research community is cautiously optimistic.
Related: We May Now Know Why Alzheimer's Erases Memories of Our Loved Ones
Today, Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and a leading cause of death in the US. Yet despite much research, no one knows how the disease starts or how to stop it from progressing.
The leading risk factor for the disease in the US appears to have shifted over the past decade.
Back in 2011, the most prominent, modifiable risk factor for Alzheimer's disease was physical inactivity, followed by depression and smoking.
According to a 2022 cross-sectional analysis, however, physical inactivity is now second to obesity when it comes to developing dementia.
"It's important that we test as many approaches as possible to tackle diseases like Alzheimer's," chief scientific officer David Reynolds from Alzheimer's Research commented in a statement.
The findings were reported in Science Advances.
An earlier version of this story was published in January 2019.