Astronomers on Wednesday confirmed the discovery of an interstellar object racing through our Solar System – only the third ever spotted, though scientists suspect many more may slip past unnoticed.
The visitor from the stars, designated 3I/Atlas by the International Astronomical Union's Minor Planet Center, is likely the largest yet detected. It has been classified as a comet.
"The fact that we see some fuzziness suggests that it is mostly ice rather than mostly rock," Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, told AFP.
Originally known as A11pl3Z before it was confirmed to be of interstellar origin, the object poses no threat to Earth, said Richard Moissl, head of planetary defense at the European Space Agency.
"It will fly deep through the Solar System, passing just inside the orbit of Mars," but will not hit our neighbouring planet, he said.
Related: What if Life on Earth Began When Interstellar Objects Crashed Here?
Excited astronomers are still refining their calculations, but the object appears to be zooming more than 60 kilometers (37 miles) a second.
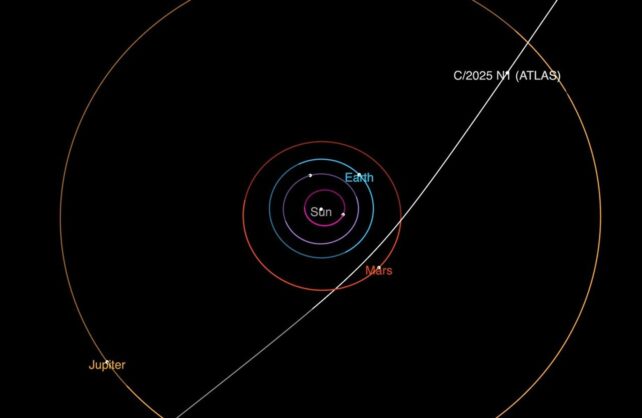
This would mean it is not bound by the Sun's orbit, unlike comets and asteroids, which all originate from within the Solar System.
Its trajectory also "means it's not orbiting our star, but coming from interstellar space and flying off to there again," Moissl said.
"We think that probably these little ice balls get formed associated with star systems," added McDowell. "And then as another star passes by, tugs on the ice ball, frees it out. It goes rogue, wanders through the galaxy, and now this one is just passing us."
The NASA-funded ATLAS survey in Hawaii first discovered the object on Tuesday, US astronomer David Rankin wrote on the social media platform Bluesky.
Was able to get my observatory open between clouds in soupy monsoon skies to nab an image of new interstellar object #A11pl3Z discovered by the Atlas team. Exciting times in astronomy. 🔭🧪
— David Rankin (@asteroiddave.bsky.social) July 2, 2025 at 1:49 PM
Professional and amateur astronomers across the world then searched through past telescope data, tracing its trajectory back to at least June 14.
The object is currently estimated to be roughly 10-20 kilometers wide, Moissl said, which would make it the largest interstellar interloper ever detected. But the object could be smaller if it is made out of ice, which reflects more light.
"It will get brighter and closer to the Sun until late October and then still be observable (by telescope) until next year," Moissl said.
Our third visitor
This marks only the third time humanity has detected an object entering the Solar System from the stars.
The first, 'Oumuamua, was discovered in 2017. It was so strange that at least one prominent scientist became convinced it was an alien vessel – though this has since been dismissed by further research.
Related: Strange Acceleration of Mysterious Interstellar Visitor Finally Explained
Our second interstellar visitor, 2I/Borisov, was spotted in 2019.
Mark Norris, an astronomer at the UK's University of Central Lancashire, told AFP that the new object appears to be "moving considerably faster than the other two extra-solar objects that we previously discovered."
The object is currently roughly around the distance from Jupiter away from Earth, Norris said.
He lamented that he would not be able to observe the object on his telescope on Wednesday night, because it is currently only visible in the Southern Hemisphere.
Norris pointed to modeling estimating that there could be as many as 10,000 interstellar objects drifting through the Solar System at any given time, though most would be smaller than the newly discovered object.
If true, this suggests that the newly online Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile could soon be finding these dim interstellar visitors every month, Norris said.
Moissl said it is not feasible to send a mission into space to intercept the new object.
Still, these visitors offer scientists a rare chance to study something outside of our Solar System.
For example, if we detected precursors of life such as amino acids on such an object, it would give us "a lot more confidence that the conditions for life exist in other star systems," Norris said.
This article has been updated.
